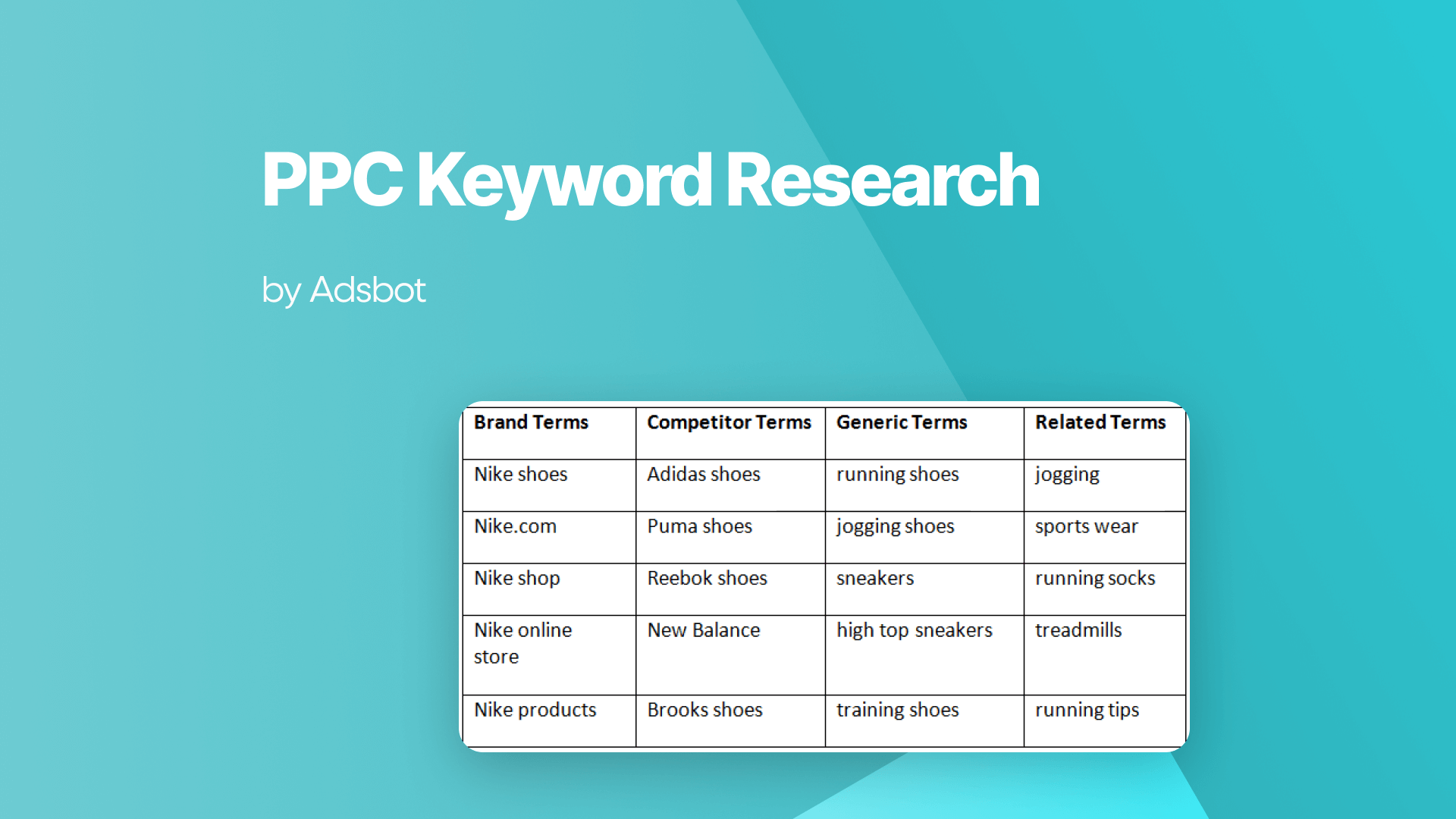
PPC keyword research is the process of finding and analyzing search terms that people enter into search engines to find products or services. This data helps advertisers select specific words or phrases to target with their paid advertisements. The primary goal is to display relevant ads to users who are actively looking for solutions, thereby increasing the likelihood of a sale or conversion.
PPC keyword research is no longer a static task of matching character strings; it is the strategic deciphering of human intent and entity relationships. In the legacy model, specific keywords triggered predictable results, much like a game of chess where every move is discrete. Today, search operates like a jazz concert: fluid, improvisational, and deeply context-dependent. AI-driven bidding systems do not just look at the word CRM; they analyze the surrounding context of the user’s journey, including location, device, past behavior, and query syntax, to predict whether they are researching features or ready to sign a contract. Keywords are no longer targets; they are signals.
We also operate in a “Search Everywhere” reality. The journey no longer begins and ends in the Google search bar. It is fragmented across a decentralized ecosystem where users seek validation on Reddit, discover solutions via social algorithms, and ask complex questions to AI assistants. To succeed, your keyword strategy must map to this multi-surface behavior, capturing demand wherever it manifests.
This guide establishes the definitive blueprint for Strategic Intent Orchestration. We move beyond vanity metrics and standard advice found in The Google Ads Keyword Guide to build high-ROI campaigns aligned with Google’s E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness). In an automated future, algorithms prioritize advertisers who demonstrate genuine expertise. By shifting your focus from volume to value, you build a resilient, defensible digital footprint.
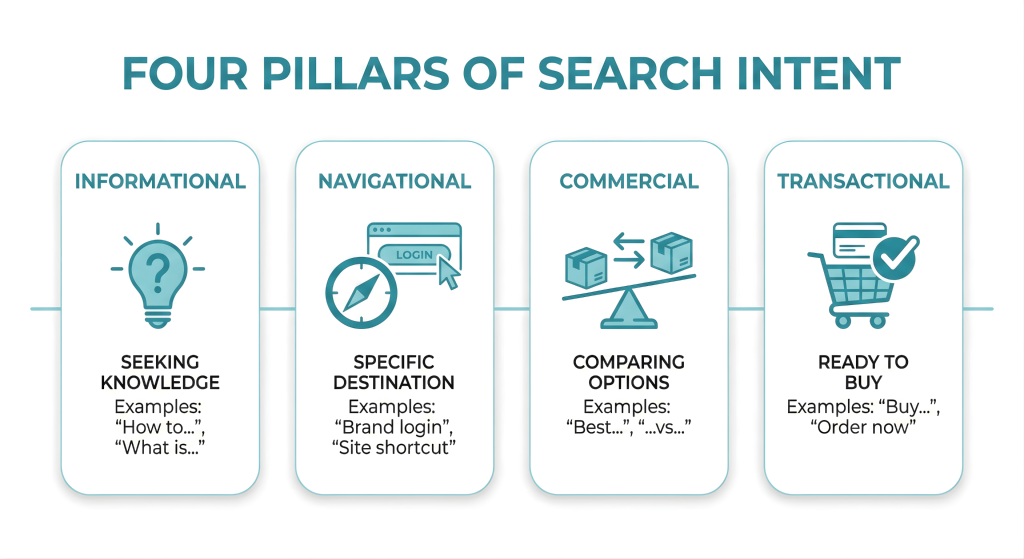
What is a Search Intent?
Search intent is simply the “why” behind a search query. It is the main goal a user has, whether they are looking for answers, trying to find a specific website, or ready to make a purchase. Understanding this motivation is essential. It helps search engines provide the right results and allows marketers to create content that meets the user’s needs at the right moment.
Types of Search Intent
There are four distinct search intents. Informational intent drives the top of the funnel; users are asking “how to” or “what is,” seeking knowledge rather than a product. Navigational intent is specific; they know the destination (e.g., “HubSpot login”) and use search as a shortcut. Commercial intent signals the “messy middle” of the journey, where users compare options (e.g., “best CRM for small business”). Finally, Transactional intent is the bottom line: the user is ready to buy (e.g., “buy iPhone 15 Pro Max”).
However, the linear progression through these stages is vanishing. We are witnessing the Funnel Collapse. AI-driven search tools and rich snippets now satisfy informational needs instantly on the SERP (Search Engine Results Page). A user can move from a broad “how to” query to a “buy now” decision in minutes, often without visiting a traditional website until the final step. This compression means your ad copy must be agile, addressing immediate pain points rather than assuming a slow, nurturing process.
Simultaneously, the syntax of search is evolving. As voice search and AI chat interfaces normalize, users are abandoning caveman speak (e.g., “cheap shoes”) for Conversational Syntax. They now ask complex, long-form questions: “What are the most durable running shoes for flat feet under $100?” These queries reveal rich, specific intent signals that broad match keywords are uniquely designed to capture. If your strategy relies solely on exact match short-tail keywords, you remain invisible to these high-value, specific inquiries.
Map your keywords to the intent funnel. Categorize your current keyword list into the four pillars. If your budget is tight, ruthlessly cut Informational queries and focus 80% of your spend on Commercial and Transactional intent. Ensure your landing pages match the intent: don’t send a “learn more” user to a checkout page, and don’t bury a “buy now” user in a blog post.
How to Find New Keywords?
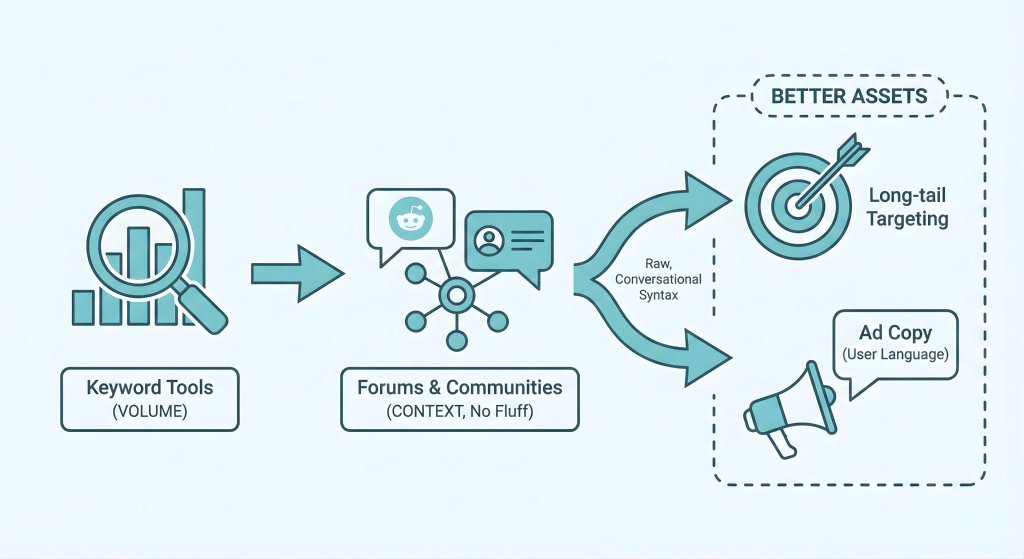
Effective keyword discovery is not an exercise in creativity; it is a process of data triangulation. You must bridge the gap between how you describe your product and how the market seeks a solution. We build this foundation using a four-quadrant approach that blends internal data with external signals.
Voice of Customer (VoC) Seed Generation
Start inside your own organization. Your sales team and customer support logs hold the most potent seed keywords. Ignore industry jargon initially and focus on utility. If you sell Enterprise Resource Planning software, your customers might be searching for “inventory management headache fix.” Review your CRM notes and live chat transcripts. What exact phrases do prospects use when describing their pain points? These voice of customer seeds often bypass the high competition of generic terms and cut straight to commercial intent.
Finding these unique angles allows you to bypass expensive bidding wars on generic terms. The goal is to identify the “whitespace” in the market: queries that are high in intent but low in saturation. For a deeper strategy on uncovering these hidden gems, we recommend reading our guide on how to find low competition keywords.
Competitor Gap Analysis & AI Share of Voice
You do not operate in a vacuum. Tools like Semrush and Ahrefs are essential for mapping the battlefield. Run a Keyword Gap analysis to identify high-value terms your top three competitors rank for, but you do not. However, in the AI era, we look deeper than rank. We analyze AI Share of Voice, which entities are consistently associated with your competitors in AI Overviews. If a competitor owns the concept of speed, and you own security, your keyword strategy must double down on security-related queries to defend that territory while attacking theirs with comparison queries (e.g., “fastest secure VPN”).
To truly excel here, you must go beyond surface-level observation and dissect your rival’s strategy to understand not just what they rank for, but why. A comprehensive audit reveals their weak spots. Learn the exact tactics in our tutorial on how to find and analyze competitor keywords, ensuring you never enter a bidding war blind.
Mining User-Generated Content (UGC)
Keyword tools show you volume; forums show you context. Platforms like Reddit and specialized industry communities are where the messy middle of the funnel happens. Users here strip away marketing fluff. They don’t ask for “best project management solutions”; they ask, “Which PM tool doesn’t lag with 50 users?” Mining these threads reveals the raw, conversational syntax discussed in Section 2. We use these verbatim phrases to inform long-tail keyword targeting and ad copy, ensuring we speak the user’s language, not a marketer’s dialect.
Predictive Modeling with Gemini & Planner
Finally, validate your findings with Google Keyword Planner, but layer it with generative AI like Gemini. Use Keyword Planner for historical volume data and seasonality. Then, feed those trends into Gemini to ask: “Based on the rising interest in [Topic A], what related sub-topics are likely to trend next quarter?” This moves you from reactive analysis to predictive strategy, allowing you to bid on emerging terms before they become expensive.
While AI adds a layer of prediction, the foundational data provided by Google’s native tools remains indispensable for accuracy. For a step-by-step walkthrough on extracting historical metrics and forecasting costs, learn how to use Google Keyword Planner. Mastering this tool ensures your predictive models are grounded in actual search reality.
Build a Seed & Gap Matrix. Create a spreadsheet with four columns: Internal Pain Points, Competitor Wins, Reddit/Forum Phrases, and AI Predictions. Populate each with 10 high-relevance terms. This 40-keyword core will serve as the anchor for your Broad Match testing.
Match Types in the AI Age
For over a decade, the Single Keyword Ad Group (SKAG) strategy reigned supreme. We obsessed over Exact Match because we believed granular control equaled efficiency. In the AI age, this logic has inverted. This is the Paradox of Precision: by rigidly defining exactly what a user must type to see your ad, you inadvertently block the highest-intent queries that you never predicted. Exact Match is no longer a sniper rifle; it is a blinder.
Broad Match
Broad match is a default keyword setting that allows your ad to appear for searches related to your keyword, even if they do not contain the exact terms. This type uses Google’s understanding of language to match ads with relevant queries, including synonyms, misspellings, and related topics. It offers the widest reach but requires careful monitoring to ensure the traffic remains relevant to your business goals.
Broad Match has shed its reputation as a budget waster. Today, it is the only match type capable of ingesting the full spectrum of Google’s signal data. While Exact and Phrase match look primarily at the query string, Broad Match analyzes the user’s recent search history, their physical location, the content of your landing page, and even the intent of other users with similar profiles. It functions less like a keyword match and more like a semantic hook, catching relevant traffic that shares the intent of your keyword, even if the words differ completely.
Smart Bidding
Smart Bidding is a subset of automated bid strategies that uses machine learning to optimize for conversions or conversion value in every auction. It analyzes millions of signals in real-time, such as device, location, and time of day, to set precise bids tailored to each unique search. The goal is to maximize performance outcomes like sales or leads while removing the guesswork of manual bidding adjustments.
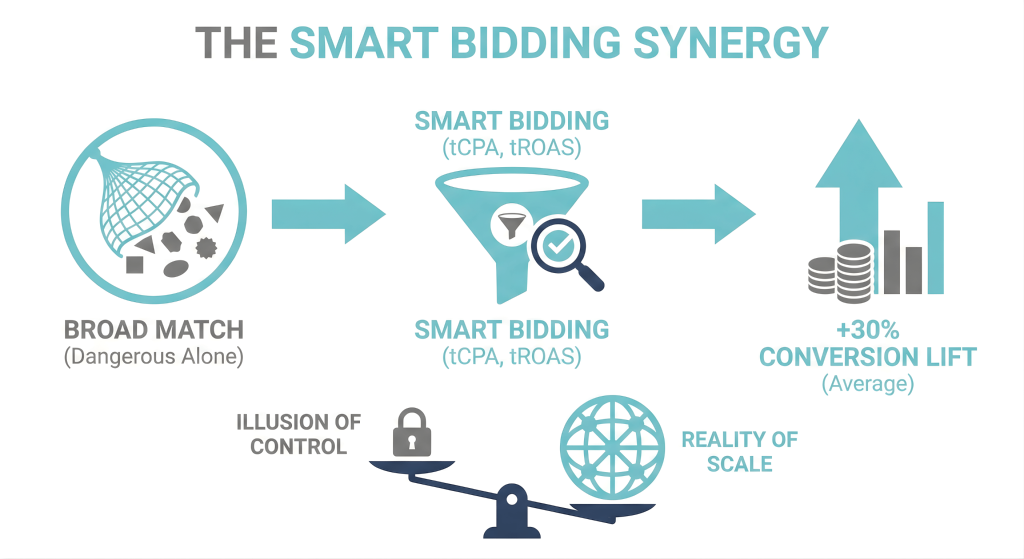
Broad Match is dangerous in isolation. It becomes a superpower only when paired with Smart Bidding strategies like Target CPA (tCPA) or Target ROAS (tROAS). This combination is non-negotiable. Broad Match casts the net wide to find inventory, while Smart Bidding acts as the filter, bidding up or down based on the probability of conversion. Google’s data consistently shows that advertisers switching from Exact to Broad Match with Smart Bidding see an average conversion lift of roughly 30%. You are trading the illusion of control for the reality of scale.
Phrase Match
Phrase Match is a keyword match type that triggers your ad only when a search query includes the meaning of your keyword. It allows the query to contain other words before or after your phrase, as long as the user’s intent matches yours. This setting offers a balance between the reach of broad match and the precision of exact match.
Is Phrase Match dead? Not yet, but its role has shrunk. Use Phrase Match selectively for terms where word order dictates semantic meaning (e.g., “flights to London” vs. “flights from London”). However, treat it as a safety net, not a default.
Take a high-performing Exact Match campaign and duplicate it. Change all keywords to Broad Match and apply at tCPA target slightly higher (more restrictive) than your historical average. Let it run for 4 weeks. You will see higher volume and new search term variations that you never would have manually mined.
Defensive Keyword Strategy
If Broad Match is the accelerator, negative keywords are the steering wheel and brakes. In the Signal Intent Orchestration model, your success is defined as much by what you exclude as what you include. Without a robust defensive strategy, you risk Signal Contamination. This occurs when Smart Bidding algorithms accidentally stumble upon low-quality traffic that converts cheaply (e.g., existing customers logging in) and then optimize aggressively toward that junk signal. Negative keywords are the only firewall against this machine learning drift.
Mastering PMax Controls
Performance Max is a goal-based campaign type that allows advertisers to access all of Google’s ad channels from a single campaign. It uses artificial intelligence to automatically show ads on YouTube, Search, Gmail, and Maps to find the best converting customers. This system optimizes bids and ad placements in real-time to maximize results across the entire Google network.
Performance Max (PMax) often feels like a black box, but recent updates have handed the keys back to strategists. You are no longer helpless. You can now apply Account-Level Negative Keyword Lists that universally block up to 1,000 bad-fit terms across all campaigns, including PMax. Furthermore, strategic use of Brand Exclusions prevents PMax from cannibalizing your branded traffic, ensuring it hunts for new customers rather than harvesting easy wins from people who already know you. Utilizing the full capacity of campaign-level exclusions (up to 10,000 negatives) allows you to sculpt traffic with unprecedented precision, blocking entire semantic clusters that don’t align with your revenue goals.
Automating the Defense With N-Gram Analysis
N-Gram analysis is a technique that breaks down search queries into smaller sequences of words to reveal hidden performance patterns. It helps you identify specific words or phrases that consistently waste money, even when they appear in different sentences. By isolating these components, advertisers can block bad traffic more effectively than by reviewing individual search terms.
Manual review of search term reports is mathematically impossible at scale. You must automate your defense using N-Gram Analysis. This technique breaks down search queries into individual words (1-grams) or pairs (2-grams) to identify patterns of waste. For example, you might find that while queries containing management convert well, any query containing “free” or “template” burns budget with zero return. We deploy simple Google Ads Scripts to monitor these N-grams 24/7. These scripts can automatically flag or exclude terms that exceed a certain CPA threshold, acting as an always-on immune system for your account. This moves you from reactive firefighting to proactive prevention.
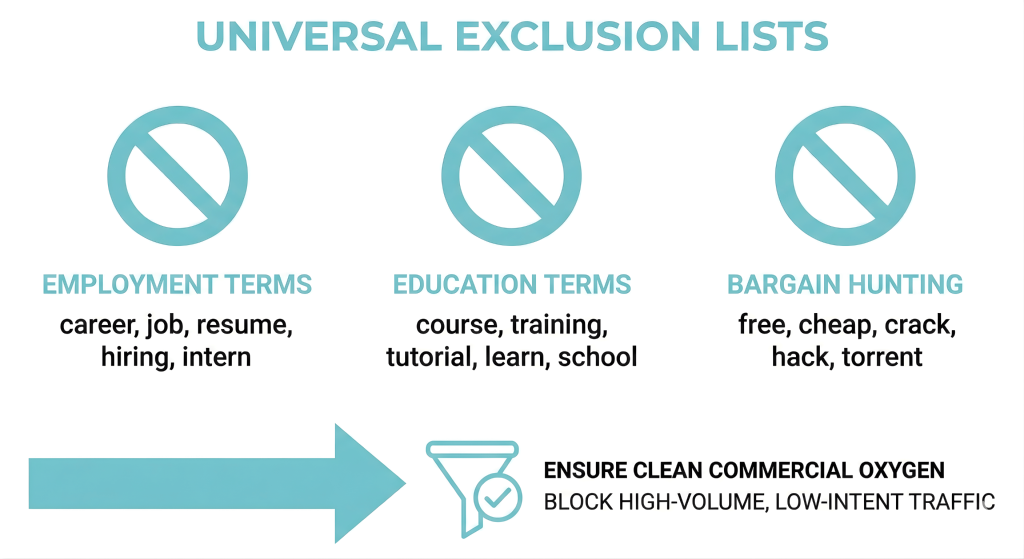
The Universal Exclusion Lists
A universal exclusion list is a set of negative keywords used across an entire ad account to stop ads from appearing for unwanted searches. It blocks specific words that rarely lead to sales, such as terms related to employment or free products. Using this list ensures that the advertising budget is focused only on relevant traffic from the very beginning.
Every account should launch with a Universal Negative List pre-applied. This includes:
- Employment Terms: career, job, resume, hiring, intern
- Education Terms: course, training, tutorial, learn, school (unless you sell courses)
- Bargain Hunting: free, cheap, crack, hack, torrent
By blocking these high-volume, low-intent signals on day one, you ensure your Broad Match keywords only breathe clean, commercial oxygen.
Implement an N-Gram Script. Don’t just look at the raw search terms. Use a script or a pivot table to analyze the performance of individual words within those queries. Identify your top 5 bleeding words, terms that appear in many queries but never convert, and add them to a Shared Negative List immediately.
Keywords for AI Agents
We are entering the age of Agentic Commerce, where the user is often a software agent acting on a human’s behalf. In this ecosystem, your keywords serve two masters: the human looking for a solution and the AI agent looking for data. An AI agent tasked with researching the best CRM for a non-profit does not browse; it extracts. It scans thousands of pages in milliseconds to find entities that match specific attributes. If your keywords are buried in unstructured text, the agent bypasses you.
Visibility now requires Machine-Readable Content. It is not enough to have the keyword “waterproof hiking boots” in your copy. You must define the attributes of those boots: price, material, weight, and availability using Schema Markup (JSON-LD). This structured code provides the context that algorithms need to confidently recommend your product. Without it, you are asking a machine to guess, and in the high-speed auction of AI search, uncertainty is a disqualifier.
This necessitates a pivot to Answer Engine Optimization (AEO). Traditional SEO was about ranking a list of blue links; AEO is about being the single correct answer. AI models prioritize content formatted as direct responses to questions. Instead of long, meandering paragraphs, structure your content around the People Also Ask questions associated with your keywords. By providing concise, factual answers to these queries, you position your brand as the citation source for AI-generated summaries.
Implement FAQ Schema. Select your top-performing commercial page. Add a Frequently Asked Questions section that addresses the top 3 objections or technical queries related to that product. Wrap this section in FAQ Schema to maximize your chances of appearing in AI-generated answers and rich snippets.
Value-Based Bidding
Value-based bidding is an automated strategy that optimizes bids to maximize the total value of conversions rather than the quantity. It analyzes data to predict the potential revenue from a user and increases bids for those likely to spend more. This ensures that advertising budget is prioritized for high-value customers who contribute most to business profit.
The era of cookie-based tracking is collapsing. We are migrating to a privacy-first ecosystem where reliance on browser pixels leaves you blind. To survive, you must own your data infrastructure. First-Party Data is now the primary fuel for intelligent keyword targeting. Google’s algorithms are voracious for signal data; if you starve them, they guess. By feeding them accurate, hashed customer lists (emails, phone numbers) via Customer Match, you explicitly identify your high-value users. This empowers you to bid aggressively on broad keywords when the searcher matches your ideal customer profile, unlocking scale without sacrificing relevance.
However, the most critical data often lives offline. A user might click an ad for “business insurance,” fill out a lead form, and then vanish from the digital view. Three weeks later, they sign a $50,000 contract. Without Offline Conversion Tracking (OCT), Google Ads views that lead exactly the same as one that was disqualified instantly. This blindness creates a race to the bottom where algorithms optimize for cheap, low-quality leads. By connecting your CRM (Salesforce, HubSpot) to Google Ads, you import that final sale value back into the system. Suddenly, the keyword “cheap business insurance” might show a $0 return, while “comprehensive liability coverage” drives all your revenue. OCT forces the algorithm to prioritize profit over volume.
This enables the critical shift to Value-Based Bidding (VBB). In the past, we optimized for Maximize Conversions (quantity). Now, we must optimize for Maximize Conversion Value (quality). You must assign dynamic values to different actions: a whitepaper download is worth $10, a demo request $100, and a closed deal $1,000. You are teaching the machine to discriminate. It will bid down on users likely to just download a PDF and bid up on users exhibiting the behaviors of a high-value buyer. This aligns your keyword strategy with business outcomes, not just marketing metrics.
Assign values to your conversion actions. Stop treating all conversions as equal. Even if you do not have perfect offline tracking yet, create a static value hierarchy (e.g., Form Fill = $50, Phone Call = $100). Switch one campaign to Maximize Conversion Value and observe the shift in traffic quality over 30 days.
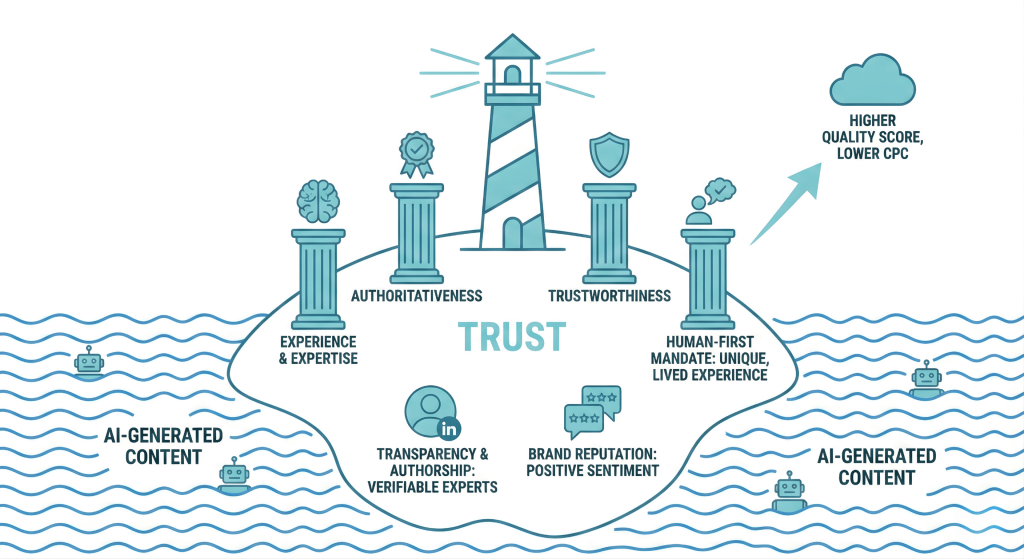
Aligning with E-E-A-T
E-E-A-T is a quality framework used by Google that stands for Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness. It serves as a standard to determine if a content creator has actual knowledge and credibility on a specific topic. Search engines prioritize content that meets these criteria to ensure users receive accurate and reliable information.
In an ocean of AI-generated content, trust is the only island. Google’s E-E-A-T framework (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness) is no longer just an SEO concept; it is a quality filter for paid search as well. Algorithms are increasingly distinguishing between commodity content, generic text that could be written by anyone, and expert content rooted in genuine experience. If your landing page looks like AI slop, your Quality Score will suffer, and your CPCs will rise.
The Human-First Mandate demands that your content demonstrates a unique, lived experience. AI can aggregate data, but it cannot replicate the nuance of a subject matter expert who has actually used the product or solved the problem. Your keywords must lead to pages that offer proprietary data, original case studies, or contrarian viewpoints that an LLM cannot hallucinate. This information gain is what signals to both users and algorithms that your page is the definitive source.
Transparency and Authorship are the mechanical levers of trust. Users (and machines) need to know who is speaking. Anonymous content is inherently suspicious. By explicitly displaying author bios, credentials, and links to LinkedIn profiles on your landing pages, you anchor your keywords to verifyable human experts. This establishes the Expertise component of E-E-A-T, validating that the advice given is credible.
Finally, Brand Reputation is now a ranking signal. AI search systems do not just scan your website; they scan the web about your website. They aggregate sentiment from third-party reviews, Reddit threads, and social chatter to determine if you are a trustworthy entity. If your ads promise excellence but the internet whispers scam, your visibility will be throttled.
Audit your “About Us” and landing page footers. Ensure every article or product page is attributed to a real person with credentials. Add a “Why Trust Us” section that highlights your years in business, awards, or editorial standards.
Building a Resilient Digital Footprint
Keyword research is no longer a set-and-forget launch task; it is a continuous cycle of calibration. As AI reshapes how users discover solutions, your strategy must pivot from static lists to dynamic signal management. The era of hoarding cheap clicks is over. The future belongs to advertisers who prioritize intent density, targeting the specific moments where search behavior signals a readiness to transact. By aligning your keywords with real-world intent and backing them with authoritative, human-centric content, you create a campaign structure that survives the shifts of automation. Don’t just capture traffic; orchestrate the outcome.
To ensure no step is missed in this complex process, systematization is key. Have a comprehensive keyword research checklist that serves as your final quality control gate before launching any campaign, ensuring every signal is optimized.
Frequently Asked Questions (F.A.Q.)
How to do PPC keyword research?
Effective PPC keyword research requires moving beyond simple list building to Strategic Intent Orchestration. Start by identifying user problems rather than just product names. Use a four-quadrant approach: audit internal customer data for seed terms, analyze competitor gaps for missed opportunities, mine user-generated content for natural language syntax, and use predictive AI to forecast trends. Finally, map these keywords to the four intent pillars (Informational, Navigational, Commercial, Transactional) to ensure you bid on revenue, not just clicks.
Can I use ChatGPT for keyword research?
Yes, but as a strategist, not a data source. Generative AI tools like ChatGPT and Gemini are excellent for Predictive Modeling. Use them to brainstorm semantic variations, identifying related topics, and predicting future trends based on current interests. However, AI tools cannot provide accurate historical search volume or CPC data. Always validate AI-generated ideas with Google Keyword Planner to ensure they have sufficient search demand.
Which tool is best for keyword research?
There is no single magic bullet; the best approach is a technology stack.
- Google Keyword Planner: Essential for accurate, historical volume data and localized metrics.
- Semrush / Ahrefs: Best for competitor gap analysis and understanding “Share of Voice.”
- Reddit / Quora: Unbeatable for discovering natural language syntax and raw user sentiment (Quadrant 3).
- Gemini / ChatGPT: Critical for lateral thinking and expanding into related semantic clusters.
How to perform keyword research step by step?
- Seed Generation: Harvest the voice of customer data from sales and support teams.
- Gap Analysis: Identify keywords your competitors rank for but you do not.
- Intent Mapping: Categorize keywords into Informational, Commercial, or Transactional buckets.
- Validation: Check search volume and CPC in Google Keyword Planner.
- Signal Testing: Launch using Broad Match with Smart Bidding to capture unpredicted variations.
- Refinement: Use N-Gram analysis to filter out low-value terms via negative lists.
What are good PPC keywords?
A good keyword is defined by intent density, not search volume. High-volume keywords often bring tire kickers with low conversion rates. The best keywords are often long-tail, specific queries that signal a readiness to act (e.g., “enterprise crm with quickbooks integration” vs. “crm software”). Prioritize keywords that map to the Commercial and Transactional stages of the funnel, as these drive direct revenue.
Can I do keyword research without tools?
Yes. You can build a potent initial list solely by reviewing internal sales transcripts, customer emails, and mining public forums like Reddit. This qualitative research often yields higher-intent terms than software tools because it reflects real human problems. However, without tools, you fly blind on search volume, seasonality, and bid estimation, making it difficult to scale or budget accurately.
Popular Posts
-
How Many Keywords Should Be In an Ad Group in Google Ads?
For the vast majority of modern campaigns, the ideal number…
Read more -
Google Ads Script for Dummies: An Introduction
Imagine you have an e-commerce website that sells licensed superhero…
Read more -
Google Ads Sitelink Character Limits
Your Google Ads are cutting off in the middle of…
Read more -
What Is Conversion Value in Google Ads?
What if you could put a price tag on every…
Read more
Register for our Free 14-day Trial now!
No credit card required, cancel anytime.